Redefining Developmental Math for Non-Algebra Core Math Courses
Redefining Developmental Math for Non -Algebra Core Math Courses
Presented at National Association for Developmental Education 32nd Annual Conference, Boston, MA, February 28, 2008
Disclaimers
• We don’t have all the answers.
• We don’t even have all the questions!
• Your mileage may vary. (It may be that nothing in this presentation will apply
to your institution’s situation.)
Current Structure
All Tennessee Board of Regents (TBR) schools use this rubric for now:
• DSPM 0700 Prealgebra
• DSPM 0800 Elementary Algebra
• DSPM 0850 Intermediate Algebra
All courses are 3 hours and do not count towards
graduation.
• Mandatory placement based on ACT or COMPASS scores
• ACT cutoff score is 19
• Students placed based on ACT may challenge placement by paying to take
COMPASS.
• Other courses: English (DSPW), Reading (DSPR); learning strategies (DSPS) if
placed in ≥ 2 areas
Placement: ACT (Current)
• Placement based on ACT subscores if scores less than 3 years old
• ACTM < 17 → DSPM 0800
• ACTM = 18 → DSPM 0850
• ACTM > 19 → MATH
• SAT equivalents : 440, 450, 460
Placement: COMPASS
• Prealgebra ≤ 29 → DSPM 0700
• 30 ≤ Prealgebra ≤ 99 and 20 ≤ Algebra ≤ 29 → DSPM 0800
• 28 ≤ Algebra ≤ 49 → DSPM 0850
• Algebra ≥ 50 → College level math
ETSU’s Situation (Here’s where your mileage may vary.)
• About 90% of our students do NOT take an algebra-based course (such as
college algebra, precalculus, calculus) for graduation. These students take MATH
1530, Probability and Statistics, as their core math class.
Redefining Developmental Math for Non‐Algebra Core Math Courses, Stephens &
Butler
• Very little intermediate algebra is used in this course.
• Mostly majors in math and the sciences take something other than prob & stat
for graduation, and they are required to take one semester of calculus. ( Digital
media majors take both P& S and trig .) These students benefit from intermediate
algebra.
Background Information (How did we get to this point?)
Defining Our Future (2002)
DSP-Specific
• Flexible delivery
• Reduce credit hours to 3 per course ( really only affected community colleges)
• Reduce DSP costs at universities to community college level.
• Align standards for high school graduation with standards for higher education
admission.
• Teach remedial (0700) courses only at community colleges.
Defining Our Future -- General
• Associate’s degree: 60 hours
• Bachelor’s degree: 120 hours
• Common calendar across TBR
• Broad common general education core for easy transferability.
Defining Our Future -- Recommended for future
consideration:
• Alternate assessments (e.g. ACT subscores)
• Revise guidelines for DSP to encourage flexibility and innovation
• Improve teacher education
• Align teacher ed, high school, college curricula
Redesign Initiative (2007+)
• TBR got large FIPSE grant to go to 5 or 6 institutions to pilot alternate
ways of delivering DSP
• Dual emphases: Cost savings and technology
• Coordinated through NCAT, National Center for Academic Transformation
NCAT’s Redesign Models
• Supplemental
• Replacement
• Emporium
• Online
• Buffet
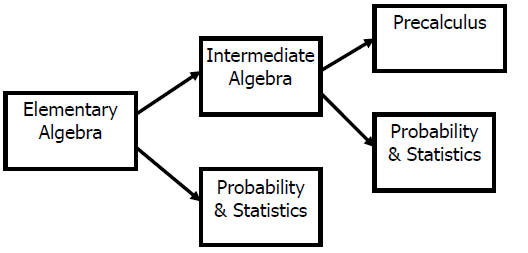
Our Redesign Proposal -- What did we think we would do?
• Re-vamp DSPM 0800 to make it a better preparation for statistics
• Delete DSPM 0850 requirement for students not taking precalculus or other
algebra-based courses
Same Topics, New Sequence
• What concepts do the statisticians think the incoming students need?
Emphasize:
• Order of operation , especially distributive property, even when using a
calculator
• Comparing (order) fractions, decimals, percents, and signed numbers
• Interpret numerical answer—(what does it mean?)
• Estimation: does the answer make sense?
• Percent, proportions, decimals
• Solving and graphing linear equations
• The language of inequalities
Our Proposal – Technology
• Use My Math Lab, Hawkes Learning, or similar programs with both courses
• Alternate days between lecture classroom and computer lab as is done with
statistics course
• Do spreadsheet activities in elementary algebra to prepare students for
Minitab
• Use graphing calculator in elementary algebra to prepare for stat and in
intermediate algebra to prepare students for precalculus
• Envisioned Advantages
• Cost savings: Cut back on sections of 0850 from ~12 each semester to ~3 or 4.
• Prepare students for courses they would actually take
• More individualized help with computer programs and developmental math tutors
Disadvantages
• Administration would be difficult
• What about students who placed in 0850? Move them on in to 1530 or put them in
0800?
• What about students who change to science major after finishing 0800→1530?
Our proposal wasn’t funded. What pilot projects were?
• Descriptions at
• Emporiums
• Paired/compressed classes
• Modularized classes
• Small class meetings, big labs
TBR DSP Redesign
• Subcommittees working in all areas including math
• Align with Tennessee high school exit standards
• This year’s 7th graders (Class of 2013) will have to take math all 4 years of
high school!
• New math curriculum standards based on NCTM, ADP, ACT, NAEP, . . .
Math Redesign Subcommittee
• Subcommittee includes university, community college, and high school faculty
• Currently surveying math and other faculty across TBR to see what math is
actually needed in intro and gen-ed courses
• Some thought given to multiple exit points
• More questions than answers at this point
Committee’s Charge
• Examine what should be taught, when, and why.
• Pilot programs help decide who, how, and where.
What to do now?
Proposed Sequences
DSPM 0800 Content (proposed)
1. Review of Real Numbers
1.2 Symbols and Sets of Numbers
1.3 Fractions
1.4 Introduction to Variable Expressions and Equations
1.5 Adding Real Numbers
1.6 Subtracting Real Numbers
1.7 Multiplying and Dividing Real Numbers-- Operations on Real Numbers
1.8 Properties of Real Numbers
2. Equations
2.1 Simplifying Expressions
2.2 The Addition and Multiplication Properties of Equality
2.3 Solving Linear Equations
2.4 An Introduction to Problem Solving
2.5 Formulas
2.6 Percent
2.8 Linear Inequalities
3. Graphing
3.1 Reading Graphs & the Rectangular Coordinate System
3.2 Graphing Linear Equations
3.3 Intercepts
3.4 Slope and Rate of Change
3.5 Slope- Intercept Form : y= mx + b
3.7 Functions
5. Exponents and Polynomials
5.1 Exponents
9. Inequalities and Absolute Value
9.1 Compound Inequalities
9.4 Linear Inequalities in Two Variables and Systems of Linear Inequalities
10. Radicals, Rational Exponents
10.1 Radicals and Radical Functions
| Prev | Next |