Elementary Algebra Review
Factoring Trinomials
Quadratic trinomials factor into the product of two binomials . Factoring
trinomials is based on the FOIL
method of multiplication. Note that the first term of the trinomial is the
product of the first terms of the
binomials. The last term of the trinomial is the product of the last terms of
the binomials. The middle
term of the trinomial is the sum of the products of the two inner terms and the
two outer terms.
To factor a quadratic trinomial, first list all possible factors for the first
term and the last term. Write out
these choices as trial factors; then find the sum of the outer and inner
products. Compare this sum to the
middle term to determine the correct factorization.
Example 1: Factor X2 – 7X + 12
The last term has a positive sign; therefore both signs are alike . The sign on
the
middle term is negative; therefore both signs are negative. The factors of X2
must
be X and X. The factors of 12 are -1, -12 or -2, -6 or -3, -4.
| Trial factors | Sum outer and inner products |
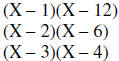 |
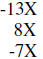 |
Therefore the answer is (X – 3)(X – 4)
Example 2: Factor 4A2 – A – 5
The last term has a negative sign; therefore one sign will be positive, and the
other will be
negative. The factors of 4A2 are A and 4A or 2A and 2A. The factors of -5 are -1
and 5 or 1 and
-5.
| Trial factors | Sum of outer and inner products |
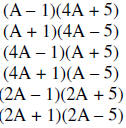 |
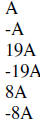 |
Therefore the answer is (A + 1)(4A – 5)
Simple Quadratic Equations
To solve quadratic equations use the Principle of Zero Products, which
states that if the product of two
factors is zero, then at least one of the factors must be zero.
| Example: Solve | 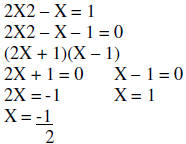 |
|
| Put into standard form | ||
| Factor | ||
| Use the Principle of Zero Products | ||
| Solve each equation | ||
The solutions are 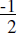 and
1.
and
1.
Exercises
Factor each of the following completely
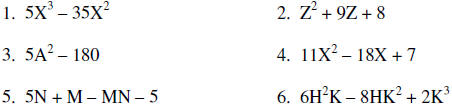
Solve each of the following questions

9. Find three consecutive positive odd integers such that
twice the product of the first two minus the
product of the first and third is 49.
10. The length of a rectangle is 3ft. more than its width.
Its area is 28 square ft. Find its dimensions.
11. A room contains 54 chairs. The number of chairs per row is three less than
twice the number of rows.
Find the number of rows and the number of chairs per row.
12. A strip of uniform width is to be cut off of both sides and both ends of a
sheet of paper that is 8
inches by 11 inches in order to reduce the size of the paper to an area of 40
square inches. Find the width
of the strip.
13. A brace wire is attached to the top of a tower 24m tall. It is anchored 7m
from the base of the tower.
How long is the piece of wire between these two points?
14. A ladder is leaning against a wall. The vertical distance up the wall to the
top of the ladder is 4ft. less
than the length of the ladder. The distance from the base of the ladder to the
wall is 8ft. less than the
length of the ladder. Find the length of the ladder.
RATIONAL EXPRESSIONS
Multiplying and Dividing Rational Expressions
Rational expressions are fractions where the numerator or the denominator or
both are polynomials . The
product of two rational expressions is a rational expression whose numerator is
the product of the
numerators and whose denominator is the product of the denominators.
| Example: |  |
|
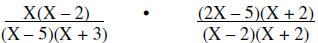 |
Factor | |
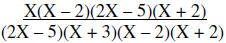 |
Multiply | |
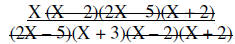 |
Simplify | |
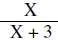 |
Write answer in simplest form |
The quotient of two rational expressions is the product of
the first rational expression and the reciprocal of
the second rational expression.
| Example: | 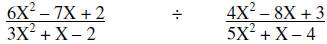 |
|
 |
Write as a multiplication problem | |
 |
Factor, Multiply, and Simplify | |
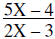 |
Write answer in simplest form |
Adding and Subtracting Rational Expressions
When adding or subtracting rational expressions with the same denominator, add
or subtract the
numerators and keep the common denominator. When adding or subtracting rational
expressions with
different denominators, first find the least common denominator for the
expressions. Next express each
rational expression in terms of the common denominator. Finally add or subtract
the rational expressions
and simplify the result.
| Example: | 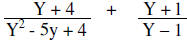 |
|
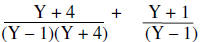 |
The denominators are factored |
The least common denominator is (Y – 1)(Y – 4)
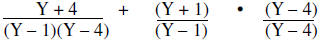 |
Express each using the LCD |
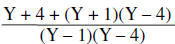 |
Add the rational expressions |
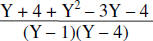 |
Simplify |
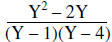 |
|
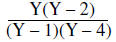 |
There are no common factors. |
Complex Fractions
When both the numerator and the denominator of a complex fraction contain a
single fraction, rewrite the
complex fraction as a division problem and do the indicated division. If the
numerator or the denominator
contain more than one term, the terms must be combined before doing the
division.
Example:
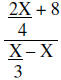
Working the numerator first
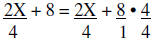 |
Rewrite using the LCD |
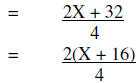 |
Add |
| Simplify | |
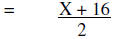 |
Working the denominator next
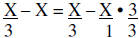 |
Rewrite using the LCD |
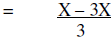 |
Subtract |
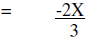 |
Simplify |
Thus
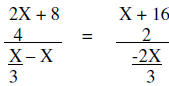 |
|
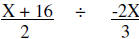 |
Write as a division problem |
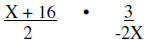 |
Write as equivalent multiplication problem |
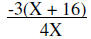 |
Multiply and Simplify |
Solving Equations with Rational Expressions
Equation containing rational expressions should first be cleared of all
denominators by multiplying every
term in the equation by the LCM of the denominators . The resulting linear or
quadratic equation is then
solved in the usual way. Always check all answers to eliminate any candidates
that result in division by
zero (excluded values).
| Example: | 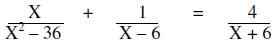 |
|
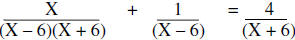 |
Factor the denominators |
The LCM of the denominators is (X – 6)(X + 6) and then multiply by the LCM
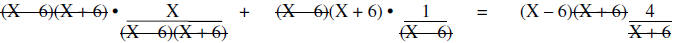
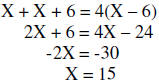 |
Resulting Equation Simplify |
Since the excluded values are 6 and -6, 15 is the solution to the equation.
| Prev | Next |
