GRADES EIGHT THROUGH TWELVE MATHEMATICS
Glossary
|
absolute value. A number’s distance from zero on the number line . The absolute value of -4 is 4; the absolute value of 4 is 4. algorithm. An organized procedure for performing a given type of calculation or solving a given type of problem. An example is long division. arithmetic sequence . A sequence of elements, 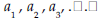 . , such that the difference of . , such that the difference ofsuccessive terms is a constant 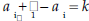 for example, the sequence 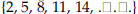 where the common difference is 3. asymptotes. Straight lines that have the property of becoming and staying arbitrarily close to the curve as the distance from the origin increases to infinity. For example, the x-axis is the only asymptote to the graph of sin(x)/x. axiom. A basic assumption about a mathematical system from which theorems can be deduced. For example, the system could be the points and lines in the plane. Then an axiom would be that given any two distinct points in the plane, there is a unique line through them. binomial. In algebra, an expression consisting of the sum or difference of two monomials (see the definition of monomial), such as 4a-8b. binomial distribution . In probability, a binomial distribution gives the probabilities of k outcomes A (or n-k outcomes B) in n independent trials for a two-outcome experiment in which the possible outcomes are denoted A and B.
dilation. In geometry, a transformation D of the parallel. Given distinct lines in the plane
that are |
binomial theorem. In mathematics, a theorem that specifies the complete expansion of a binomial raised to any positive integer power. box-and-whisker plot. A graphical method for showing the median, quartiles, and extremes of data. A box plot shows where the data are spread out and where they are concentrated. complex numbers . Numbers that have the form a + bi where a and b are real numbers and i satisfies the equation i2 = -1. Multiplication is denoted by (a+bi)(c+di) = (ac-bd) + (ad+bc)i, and addition is denoted by (a+bi) + (c + di) = (a+c) + (b+d)i. congruent. Two shapes in the plane or in space are congruent if there is a rigid motion that identifies one with the other (see the definition of rigid motion). conjecture. An educated guess. coordinate system. A rule of correspondence by which two or more quantities locate points unambiguously and which satisfies the further property that points unambiguously determine the quantities; for example, the usual Cartesian coordinates x, y in the plane. cosine. Cos(θ) is the x-coordinate of the point on the unit circle so that the ray connecting the point with the origin makes an angle of θ with the positive x-axis. When θ is an angle of a right triangle, then cos(θ) is the ratio of the adjacent side with the hypotenuse.
histogram. A vertical block graph with no spaces reflection. The reflection through a line
in the
|
|
sine. Sin(θ) is the y-coordinate of the
point on the unit circle so that the ray connecting the point with the origin makes an angle of θ with the positive x-axis. When θ is an angle of a right triangle, then sin(θ) is the ratio of the opposite side with the hypotenuse. square root. The square roots of n are all the numbers m so that m2 = n. The square roots of 16 are 4 and -4. The square roots of -16 are 4 i and -4 i. standard deviation. A statistic that measures the dispersion of a sample. symmetry. A symmetry of a shape S in the plane or space is a rigid motion T that takes S onto itself (T(S) = S). For example, reflection through a diagonal and a rotation through a right angle about the center are both symmetries of the square. system of linear equations. Set of equations of the first degree (e.g., x + y = 7 and x - y = 1). A solution of a set of linear equations is a set of numbers 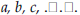 . so that when the variables . so that when the variables |
are replaced by the numbers all the equations are satisfied. For example, in the equations above, x = 4 and y = 3 is a solution. translation. A rigid motion of the plane or space of the form X goes to X + V for a fixed vector V. transversal. In geometry, given two or more lines in the plane a transversal is a line distinct from the original lines and intersects each of the given lines in a single point. unit fraction. A fraction whose numerator is 1 (e.g., 1⁄π, 1⁄3, 1⁄x). Every nonzero number may be written as a unit fraction since, for n not equal to 0, n = 1/(1/n). variable. A placeholder in algebraic expressions; for example, in 3x + y = 23, x and y are variables. vector. Quantity that has magnitude (length) and direction. It may be represented as a directed line segment. zeros of a function. The points at which the value of a function is zero. |
| Prev | Next |
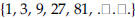 the common ratio
the common ratio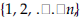 is a reordering of these
is a reordering of these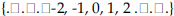 .
.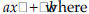 x is variable and a and b are
x is variable and a and b are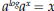 .
.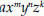 , in which
m,
, in which
m,