Calculator Comparison Guide
| TI-82 | TI-83+ | TI-85 | TI-86 | |
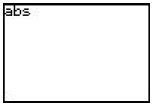
| Absolute Value | [2nd], <ABS>. Shows abs on the screen, does not put a parenthesis.
|
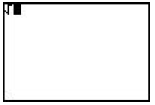
[2nd], <CATALOG>, [ENTER]. Can also be accessed by [ MATH ], right arrow to NUM, press [ENTER] to access 1:abs( Shows abs( on the screen, enters a left parenthesis. 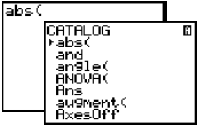 |
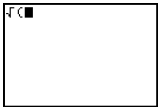
[2nd], <CATALOG>, [ENTER] to access abs. A parenthesis is not automatically entered. Can also be accessed under [2nd], <MATH>, [F1] to access NUM, [F5] to access abs. 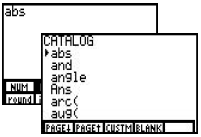 |
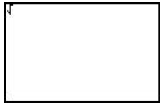
[2nd], <CATLG-VARS>, [F1] to access CATLG, [ENTER] to access abs. A parenthesis is not automatically entered. Can also be accessed under [2nd], <MATH>, [F1] to access NUM, [F5] to access abs. 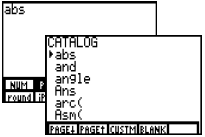 |
| Square Root | Press [2nd], <•>. A parenthesis is not displayed after the square root symbol .
|
Press [2nd], <•>. A parenthesis is displayed after the square root symbol .
|
Press [2nd], <•>. A parenthesis is not displayed after the square root symbol.
|
Press [2nd], <•>. A parenthesis is not displayed after the square root symbol.
|
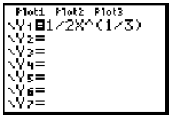
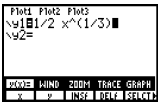
| Cube Root | Press [MATH], 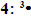 .
A .
Aparenthesis is not displayed.
|
Press [MATH],
A parenthesis is displayed.
|
See next row. | See next row. |
| Nth Root Will take any designated root of a radicand. |
Enter the root number, press [MATH], 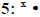 . .A parenthesis is not displayed.
|
Enter the root number, press [MATH], 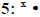 . .A parenthesis is not displayed.
|
Enter the root number, press [2nd], <MATH>, [F5] to access MISC, [MORE], [F4] to access 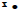 . Can also be . Can also beaccessed by [2nd], <CATALOG>, arrow up until you reach 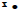 . A parenthesis . A parenthesisis not displayed.
|
Enter the root number, press [2nd], <MATH>, [F5] to access MISC, [MORE], [F4] to access 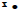 . Can also be . Can also beaccessed by [2nd], <CATLG VARS>, arrow up until you reach 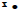 A parenthes is is not displayed.
|
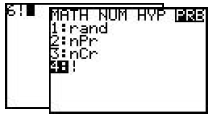
| Factorial | Press [MATH], arrow right to PRB, arrow down to 4:!, press [ENTER].
|
Press [MATH], arrow right to PRB, arrow down to 4:!, press [ENTER].
|
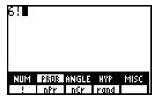
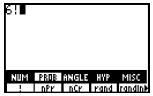
Press [2nd], <MATH>, [F2] to access PROB, [F1] to access !.
|
Press [2nd], <MATH>, [F2] to access PROB, [F1] to access !.
|
| Change a Decimal Answer to a Fractional Answer if the Number is Rational |
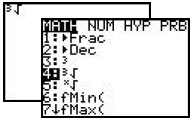
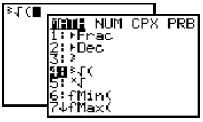
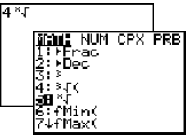
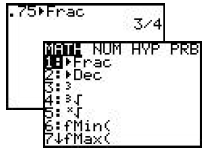
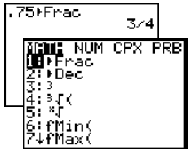
Press [MATH], 1:Frac, [ENTER].
|
Press [MATH], 1:Frac, [ENTER].
|
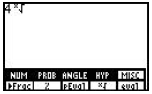
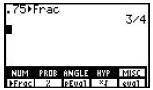
[2nd],<MATH>, [F5] to access MISC, [MORE], [F1] to access Frac, [ENTER]. Can also access by [2nd], <CATALOG>, arrow up until you reach Frac.
|
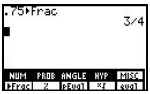
[2nd], <MATH>, [F5] to access MISC, [MORE], [F1] to access Frac, [ENTER]. Can also access by [2nd], <CATLG-VARS>, [F1] to access CATLG. Arrow up until you reach Frac.
|
| Parentheses Needed with Fractions used as Coefficients or Exponents |
Both coefficients and exponents must be in parentheses.
|
Fractional coefficients do not have to be in parentheses, but fractional exponents do.
|
Both coefficients and exponents must be in parentheses.
|
Fractional coefficients do not have to be in parentheses, but fractional exponents do.
|
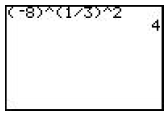
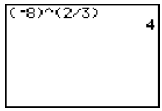
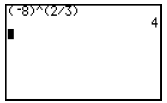
| Raising a Negative Base to a Rational Exponent with a Numerator • … 1 i. e. 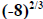 |
Negative base must be in parentheses and exponent must be separated into two parts, one representing the root (•) and the other representing the power (2).
|
Negative base must be in parentheses, fractional exponent must be in parentheses, but may be entered as a single fraction.
|
Negative base must be in parentheses and exponent must be separated into two parts, one representing the root (•) and the other representing the power (2).
Entering the exponent as a
|
Negative base must be in parentheses, fractional exponent must be in parentheses, but may be entered as a single fraction.
|
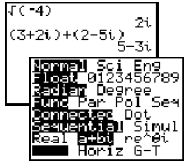
| Complex Numbers | Not available. | The key to enter imaginary numbers, i, is located above the period key. Under [MODE], the calculator can be changed to give complex answers by highlighting a + bi instead of Real.
Press [MATH], right arrow
|
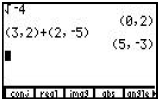
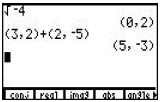
A complex number a + bi is entered as (a, b). Press [2nd] <CPLX> to display a menu of operations .
|
A complex number a + bi is entered as (a, b). Press [2nd] <CPLX> to display a menu of operations.
|
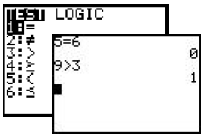
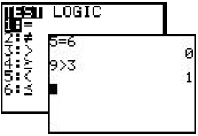
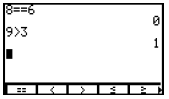
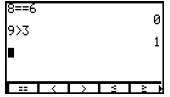
| Test Menu Allows you to test for equality or inequality. If the test is true, a 1 will appear. If the test is false, a 0 will appear. |
Press [2nd], <TEST>.
|
Press [2nd], <TEST>.
|
Press [2nd], <TEST>.
|
Press [2nd], <TEST>.
|
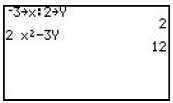
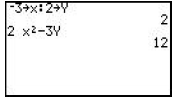
| Storing Values Allows you to store values for variables, used in evaluating an expression. |
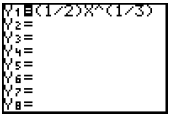
Enter the value to be stored , press the [STO•]. If the value is to be stored for x, press [X,T,è]. If the value is to be stored for a different variable, press [ALPHA] and then the key with the appropriate letter written above. If more than one value is to be stored, each can be entered on the same line , separated by a colon. These values will now be used for these variables , until other values are stored.
|
Enter the value to be stored, press the [STO•]. If the value is to be stored for x, press [X,T,è,n]. If the value is to be stored for a different variable, press [ALPHA] and then the key with the appropriate letter written above. If more than one value is to be stored, each can be entered on the same line, separated by a colon These values will now be used for these variables, until other values are stored.
|
Enter the value to be stored, press the [STO•]. If the value is to be stored for x, press [x-VAR]. If the value is to be stored for a different variable , press [ALPHA] and then the key with the appropriate letter written above. If more than one value is to be stored, each can be entered on the same line, separated by a colon These values will now be used for these variables, until other values are stored.
|
Enter the value to be stored, press the [STO•]. If the value is to be stored for x, press [x-VAR]. If the value is to be stored for a different variable, press [ALPHA] and then the key with the appropriate letter written above. If more than one value is to be stored, each can be entered on the same line, separated by a colon These values will now be used for these variables, until other values are stored.
|
| Prev | Next |