Third Grade Math Vocabulary
Third Grade
| Area: The number of nonoverlapping units that cover a closed boundary (measured in square units ). |
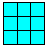 The area
of this square is 9 square units. The area
of this square is 9 square units. |
| Array: An arrangement of objects in a regular pattern, usually rows and columns. Arrays are commonly used to model multiplication. |
 This array has 2 rows and 5 columns. So, 2 × 5 = 10. |
| Benchmark Fraction: A fraction which is easily recognizable and can be used to estimate the size of other fractions or to compare other fractions. (ie, ½, ¼, ¾ ) |
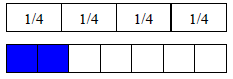 2/7is close in size to1/4. |
| Capacity: The amount of liquid or dry matter that a container can hold. |
The gas container has a capacity of 5 gallons.  |
| Common Equivalencies: Units within measurement systems that are equal and can be substituted for each other. (For example, 4 quarts equal 1 gallon, 100 centimeters equal 1 meter, 16 ounces equal 1 pound) |
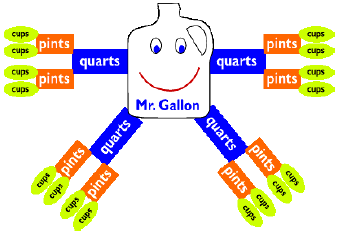 |
| Commutative Property: A property of addition and multiplication (but not of subtraction and division ) that says that changing the order of the numbers being added or multiplied does not change the answer. |
3 + 6 = 6 + 3 3 − 6 ≠ 6 − 3 8 × 2 = 2 × 8 8 ÷ 2 ≠ 2 ÷ 8 |
| Conclusion: A sensible decision reached after looking at many facts. |
After looking at the pattern 3, 8, 13, 18, 23,… , the conclusion was made that the next number is 28 based on the observation that 5 was being added each time. |
| Congruent Figures: Figures that have exactly the same shape and size. |
Congruent Pentagons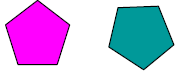 These pentagons are the same size and the same shape. One will fit exactly over the other. |
| Conjecture: A guess about an outcome before all the facts are known. |
After looking at many examples, students made the
conjecture that order doesn’t matter when adding, but is important when subtracting. |
| Data: Information that is gathered by counting, measuring, asking questions, or observing. A collection of facts from which conclusions may be drawn. |
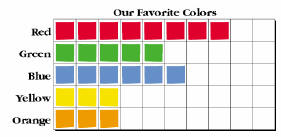 |
| Decimal: A number that uses place value and a decimal point to show tenths and hundredths. |
The decimal 0.3 is read as three-tenths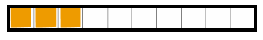 |
| Denominator: The number below the bar in a fraction that tells the number of equal parts in the whole. Numerator: The number above the bar in a fraction which represents the number of equal parts being considered. |
In the fraction ¾, the numerator is 3, the denominator is 4. This fraction tells you that you have 3 out of four parts. 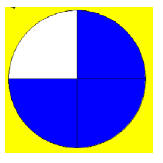 |
| Distributive property : A property that relates multiplication and addition or subtraction. This property gets its name because it “distributes” a factor over terms inside parentheses. |
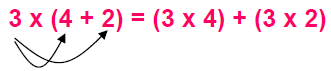 |
| Division: The process of determining how many equal groups can be made from a quantity. Division is the inverse of multiplication. |
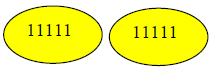 10 divided by 5 equals 2. (How many groups of 5 are in 10? There are two groups of 5.) |
| Elapsed time: The amount of time taken to go from a start time to a finish time. |
The soccer game started at 5:30 P.M. The game was
over at 6:15 P.M. The elapsed time was 45 minutes. It took a total of 45 minutes to play the game. |
| Equation: A number sentence that contains an equal sign. |
7 + x = 10 and 25 = 29 − ϑ are both equations. |
| Equivalent Fractions : Fractions that have different denominators but name the same amount. |
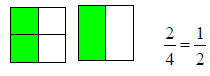 |
| Estimation: An answer that should be close to an exact answer. |
53 + 38 can be estimated as 50 + 40 = 90 |
| Expanded Form : A numeral showing the sum of values of each digit. Standard Form A numeral shown as the sum of its place value addends is standard form. |
50,000 + 3,000 + 200 + 5 = 53,205 (expanded form) (standard form) |
| Factor: Any of the numbers that are multiplied to find a product. |
5×3 = 15 5 and 3 are factors and 15 is the product. |
| Frequency Table: Data which shows the amount of times that a number occurs. |
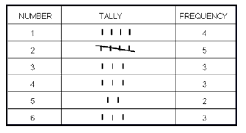 |
| Graph (using different types): A picture representation of data such as bar graphs, line plots, pictographs and frequency tables. |
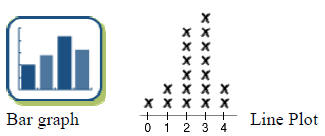 |
| Justify: To demonstrate that a statement is correct or valid. To give a reason to support an answer. |
Find the next number in the pattern and justify
the answer: 98, 87, 76, 65, … The next number is 54
because you subtract 11 each time to |
| Line of Symmetry: A line drawn through a figure that divides the figure into two parts that are mirror images of each other. When you fold a figure along its line of symmetry, both parts match. |
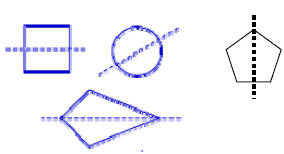 |
| Line Plot: A sketch of data in which check marks, Xs, or other marks above a labeled line show the frequency of each value. |
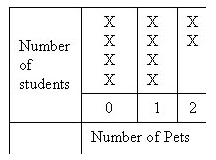 |
| Measurement: A number used to describe the quantity, dimension, weight, or capacity of an object. |
The measurements of the room were 10 ft by 12 ft,
so the area was 120 square feet. 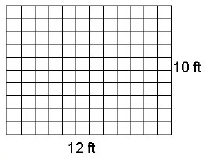 |
| Metric system: A measurement system based on the base-ten numeration system. |
10 millimeters = 1 centimeter 100 centimeters = 1 meter 1000 milliliters = 1 liter |
| Multiple: A number is a multiple of a given number if it is evenly divisible by that number. If you skip count by fours from 0, you name multiples of 4. |
0, 3, 6, 9, and 12 are multiples of 3. 0, 25, 50, 75, and 100 are multiples of 25. |
| Number Sentence: A complete numerical statement using mathematical symbols demonstrating an equality or an inequality. |
12 = 9 + 3 and 15 + 30 + 50 < 100 are number sentences. |
| Ounce/ Gram: Units used to measure weight. |
Small weights are measured in ounces or
milligrams and heavier weights are measured in pounds or grams. |
| Parallel/ Perpendicular/ Intersecting Lines: Parallel lines are always the same distance apart, and never meet or cross. Perpendicular lines meet at right angles. Intersecting lines meet or cross one another. |
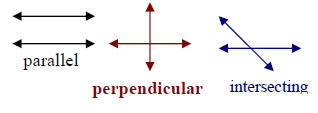 |
| Perimeter: The distance around a closed 2-dimensional shape. |
The perimeter of the triangle is 12 units. 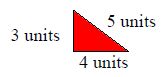 |
| Pictograph: A graph that uses pictures or symbols to represent numbers. |
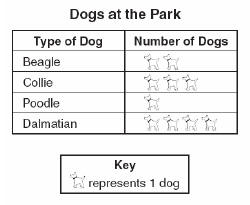 |
| Place value: A system for writing numbers in which the value of a digit depends on its place in the number. |
The 5 in the number 25,692 has a place value of 5 thousand. |
| Plane/ Solid Figures: Plane figures are two-dimensional shapes such as rectangles, squares and circles . Solids are three-dimensional shapes such as prisms, pyramids and spheres. |
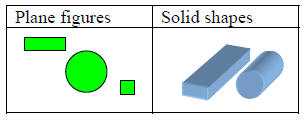 |
| Probability (conceptual): The possibility that an event will happen. |
Terms used to describe probability are likely,
unlikely , certain, possible or impossible. |
| Properties: Basic characteristics. |
Three properties of squares are that they have
four sides, are equilateral and have four right angles. |
| Survey: A gathering of a sample of data. A method of gathering information by questioning people in a poll. |
Chris took a survey to find the favorite lunch of students in the cafeteria. 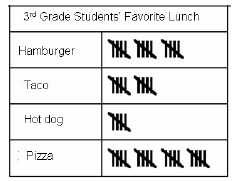 |
| Three-Dimensional: Solid objects that have length, width, and height and take up space. They have surface area and volume. |
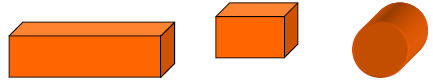 |
| Two-Dimensional figures: Flat shapes that have only two dimensions, length and width (plane figures). They have area, but do not have volume. |
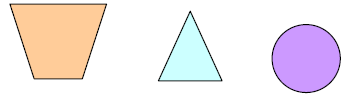 |
| Unit Fraction: A fraction that has a numerator of one. |
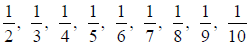 are unit fractions |
| Prev | Next |