Equations and Inequalities
The exam will be based upon your homework, the material we
covered in class, along with
the material in the textbook. It will be in class on Thursday, March 5, and you
will have
seventy five minutes to complete it. This study guide provides an overview of what
will be
on the exam.
Chapter 3.1 Reading Graphs, Plotting Points, and
Scaling Graphs. Students
should be able to perform each of the following tasks:
(1) Use graphs to answer questions and problem solve
(2) Use and de ne the following vocabulary: graph, plot, axes, coordinates,
ordered
pairs, x- and y-axes
(3) Plot points and label the four quadrants of a coordinate plane
(4) Use the window operation on the TI to change the viewing window
Chapter 3.2 Graphing Equations. Students should be able to
perform each of the
following tasks:
(1) Determining if an ordered pair is a solution to an
equation
(2) Graph linear equations by plotting solutions (box p 176)
(3) Graph equations using the TI : Y=, ZOOM, GRAPH
Chapter 3.3 Linear Equations and Intercepts. Students
should be able to perform
each of the following tasks:
(1) Know the Standard Form of a Linear Equation Ax + By =
C and that all linear
equations can be written in this form.
(2) Find Intercepts: y- intercept is where x = 0, x-intercept is where y = 0
(3) Use intercepts to graph an equation
(4) Read and graph vertical and horizontal lines: Ax = C vs. By = C
Chapter 3.4 Rates. Students should be able to perform each of the following tasks:
(1) Know that a rate is a ratio that indicates how two
quantities change with respect
to each other
(2) Find the units associated with a rate
(3) Find a rate (including units) in a given a word problem
(4) Visualize rates by graphing the information given in a word problem
Chapter 3.5 Slope. Students should be able to perform each of the following tasks:
(1) Know that rate and slope are related
(2) Read the slope o of a given graph
(3) Know the formula for slope :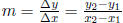
(4) Recognize the equations and graphs of both horizontal and vertical lines.
Horizontal
lines have a slope of zero , vertical lines have an undefined slope
Chapter 3.6 Slope-Intercept Form. Students will be able to
perform each of the fol-
lowing tasks :
(1) Graph a line using the y-intercept and slope
(2) Know the Slope-Intercept form of the line: y = mx + b
(3) Graph a given an equation of a line (standard form or slope-intercept)
(4) Know that two lines with different y -intercepts are parallel if they have the
same
slope
(5) Know that two lines with different y-intercepts are perpendicular if the
product of
their slopes is -1
(6) Find and graph a second line that is parallel or perpendicular to a given
line
(7) Use the TI to square the window : ZOOM ⇒ 5:ZSquare
Chapter 3.7 Point-Slope Form; Introduction to Curve
Fitting . Students will be
able to perform each of the following tasks:
(1) Understand the Point-Slope equation: y - y0 = m(x -
x0)
(2) Given a point and a slope, find the equation of the line
(3) Find a line that is parallel (perpendicular) to a given line that passes
through a
particular point
(4) Find an equation for the line that passes through two given points
(5) Use interpolation and extrapolation to calculate the coordinates of an
unknown
point
(6) Plot data points using the TI STAT ⇒ EDIT ⇒
1:Edit...
(7) Find the line of best t using the linear regression opperation on the TI:
STAT ⇒
CALC ⇒ 4:LinReg(ax+b) ⇒
LinReg(ax+b) L1,L2,Y1
Chapter 3.8 Functions. Students will be able to perform each of the following tasks:
(1) The definition of a relation vs. the definition of a
function
(2) Determine if a relation is a function
(3) Vertical Line Test
(4) Find the domain and range of a relation/function (Use set-builder or
interval no-
tation and graph)
(5) Find the output of a piecewise-defined function
(6) Apply knowledge of linear equations to solve application problems
Remember the five problem solving steps: Familiarize, Translate, Carry Out, Check, State
| Prev | Next |