From Rational to Factorial
A factorial number N denoted by N = [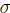 , a,
b] consists of three parts.
, a,
b] consists of three parts.
• the sign part 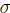 which is either 0 or 1,
which is either 0 or 1,
• the whole part a = [an, . . . , a1, a0], where ak = 0, 1, . . . , k + 1, for k
= 0, 1, . . . , n and,
• the fractional part b = [b1, b2, . . . , bm], where bk = 0, 1, . . . , k for k
= 1, 2, . . . ,m
such that N is equivalent to the decimal number
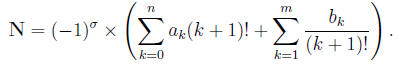
For example, the factorial number [1, [3, 2, 1, 1, 1, 0], [0, 0, 2, 2]] is equivalent to
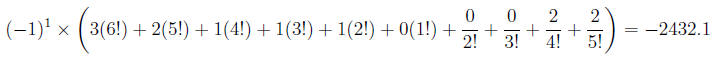
which is equivalent to the rational number -24321/10 or 24321/-10.
It can be shown that any rational number can be represented uniquely by a
factorial
number of the form [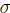 , a, b] where a and b are of finite lengths.
, a, b] where a and b are of finite lengths.
Write a program that converts a rational number to a factorial number.
INPUT
One line of input per case. The line represents a rational number R in the form
n/d where n
and d are integers with d not equal zero .
OUTPUT
One line of output per test case. The line represents the factorial number
that corresponds
to the rational number in the input. It must have the form
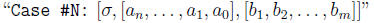
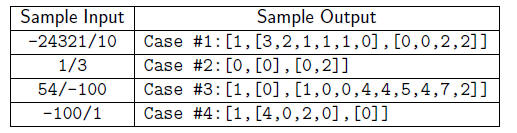
| Prev | Next |