LINEAR EQUATIONS
Definitions
Like terms are terms that have the same
variables with the same exponents
2x, 7x
− 5x2, 8x2
Unlike terms have different variables or different
exponents on the variables .
2x, 7
− 5x3 , 6x2
Properties of the Real Numbers
| a(b + c) = ab + ac | Distributive property |
| a + b = b + a | Commutative property of addition |
| ab = ba | Commutative property of multiplication |
| (a + b) + c = a + (b + c) | Associative property of addition |
| (ab)c = a(bc) | Associative prop |
8x + 4x = (8 + 4)x = 12x
5y− 6y = (5 − 6)y = −y
x + 15 − 5x + 9 = (1− 5)x + (15+9) = −4x + 24
1 3x + 2 + 6y − 4 + 7x = (3 + 7)x + 6y + (2 − 4) = 10x + 6y − 2
Addition and Multiplication Properties of
Equality
Addition Property of Equality
For all real numbers A, B, and C, the equations
A = B and A + C = B + C
are equivalent .
That is, the same number may be added to each side of an
equation without changing the solution set.
Multiplication Property of Equality
For all real numbers A, and B, and for C ≠ 0, the equations
A = B and AC = BC
are equivalent.
That is, each side of the equation may be multiplied by the
same nonzero number without changing the solution set .
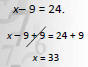 |
Use addition property to “move” 9 to the other side |
| “undo” subtraction with addition |
Check: x− 9 = 24
33 − 9 = 24 ?
24 = 24 true
Find the solution to the equation
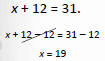 |
Use the addition Property to “move” 12 to other side. |
| “undo” addition with subtraction |
Check: x+ 12 = 31
19 + 12 = 31 ?
31 = 31 true
Multiplication Property of Equality
For all real numbers A, and B, and for C ≠ 0, the equations
A = B and AC = BC
are equivalent.
That is, each side of the equation may be multiplied by the same nonzero number
without
changing the solution set.
Find the solution to the equation
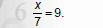 Use Multiplication Property
Use Multiplication Property
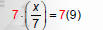 “Undo” division with multiplication
“Undo” division with multiplication
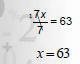
Division Property of Equality
For all real numbers A, and B, and for C ≠ 0, the equations
A = B and
are equivalent.
That is, each side of the equation may be divided by the same nonzero number
without
changing the solution set.
Find the solution to the equation
4x = 48  “Undo” multiplication with division
“Undo” multiplication with division
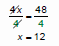
Strategies for Solving Linear Equations
1. Eliminate fractions : multiply both sides by LCD or
Multiply LCD by each term.
2. Remove ( ) or grouping symbols using the Distributive
property.
3. Combine Like terms.
4. Move variables to same side.
5. Isolate the variable.
Solve 3x− 4 = 17
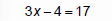 |
“Undo” subtraction with addition |
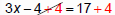 |
|
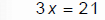 |
“Undo” multiplication with division |
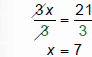 |
Solve 21 = 6 + 3(x + 2)
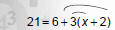 |
1. Remove () using the distributive property. |
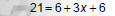 |
2. Combine like terms |
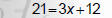 |
3. “Undo” addition with subtraction. |
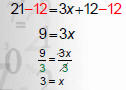 |
Solve 8x + 3 = 6x + 21
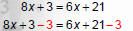 |
1. Move variables and constants to the same side. |
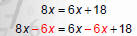 |
|
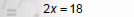 |
2. Undo multiplication
with division |
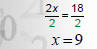 |
Solve 6(x− 2) + 2x + 3 = 4(2x − 3) + 2
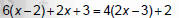 |
1. Remove () with distributive Property. |
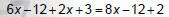 |
2. Combine like terms. |
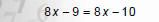 |
3. Move variables to one side and constants to the other. |
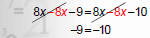 |
NOTICE: The variable disappeared! |
‐9 does not equal ‐10!!!
A FALSE statement means the equation has no solution.
Therefore, equation is inconsistent.
Solve 4(x + 1) − 6(x + 2) = −2(x + 4)
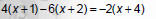 |
1. Remove () with distributive Property. |
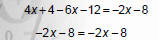 |
2. Combine like terms. |
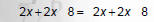 |
3. Move variables to one side and constants to the other. |
 |
NOTICE: The variable disappeared! |
Since the statement is true,
0 = 0 or ‐8 = ‐8, the solution is all real
numbers.
| Prev | Next |