POLYNOMIALS AND RATIONAL EXPRESSIONS
Polynomial in standard form:
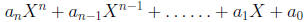
where n ≥ 0 is an integer and
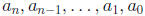 are constants
are constants
called the coefficients.
A polynomial with one term is called a monomial:
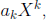
where k is a whole number. The monomials that form a poly-
nomial are called terms.
For a polynomial
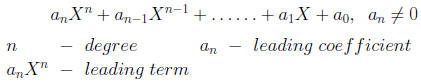
Polynomial? Yes/No Coefficients Degree
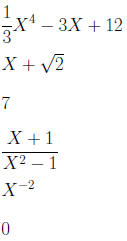
Adding and Subtracting Polynomials
Polynomials are added and subtracted by combining the
mono -
mials that may differ only by coefficients.
Example: Perform the indicated operations
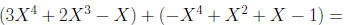
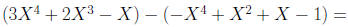
Multiplying Polynomials
Two polynomials are multiplied by using the Properties of Real
Numbers and Laws of Exponents .
Example: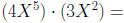
Find the product:
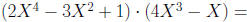
Special Products
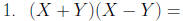
Evaluate: (2a + 3)(2a − 3) =
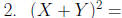
Evaluate: 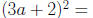
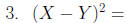
Evaluate: 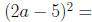
Factoring is the process of expressing a polynomial as a
prod-
uct of two or more nontrivial polynomials.
Example: 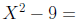
A polynomial is called prime or irreducible if it cannot
be
written as a product of two nontrivial polynomials.
Factoring out the common factor
Factor the following:
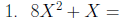
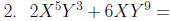
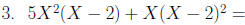
Factoring by grouping
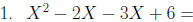
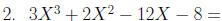
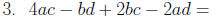
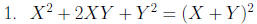
Factor: 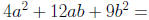
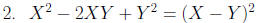
Factor: 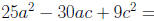
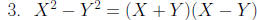
Factor: 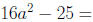
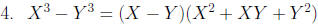
Factor: 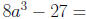
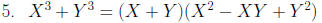
Factor: 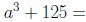
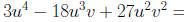
A rational expression is a quotient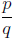 of
two polynomials,
of
two polynomials,
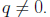
Example: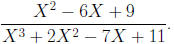
Simplify Rational Expressions
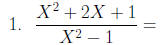
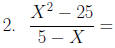
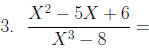
Multiplication and Division of Rational Expressions
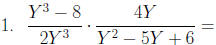
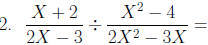
Addition and Subtraction of Rational Expressions
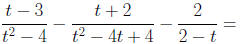
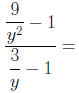
| Prev | Next |