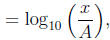Logarithmic Functions
GOAL: Learn logarithmic functions as inverses of exponential functions and
use them to model various
interesting situations, like intensity of earthquake, noise level, and acidity
of beer.
Q1: What “undoes” the exponential function
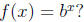 (e.g. If
(e.g. If
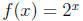 then
then
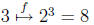 )
)
A1: The logarithmic function with base b, denoted
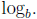 (If
(If
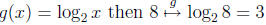 )
)
Definition:
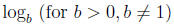 is defined by
is defined by

Example 1 Express the following logarithms as an integer or fraction without using a calculator.
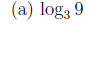
•The graph of log bx for b > 1:
As an example, first graph y = 2x and obtain the graph of y = log2x.
Properties of logarithmic functions

• It’s continuous and increasing.

Note: The most common choices for b are 10, e and 2 .
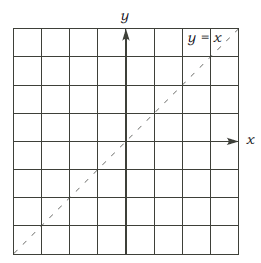
• The laws of logarithms . (Reversing the laws of exponents) Let s, t > 0. Then
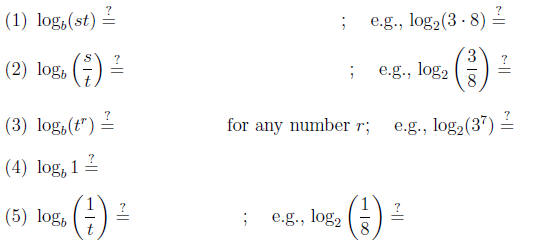
Q2: Can you explain property (1)?
A2:
Example 2 Use the approximation log100.5 ≈ −0.301 to estimate log1020.
Example 3 Use the approximation log23 ≈ 1.585 and log25 ≈ 2.322 to estimate log245.
Example 4 Suppose A and b are positive numbers with log3A =
b. Write
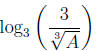 in
terms of b .
in
terms of b .
Example 5 A bank teller claims that a saving account with principal of
$1000 earning interest at a
annual rate of 1.3 %, compounded weekly , after T years would at least double.
What is the smallest
possible T in whole years?
• Logarithms with base 10
Logarithms with base 10, called common logarithms , are used in many well-known applications.
1 The Richter scale
where A is the amplitude of the seismic wave of a reference earthquake and x
is the amplitude of the
seismic wave of the earthquake in question.
Example 6 One of the worst earthquakes in history occured in Tokyo and
registered 8.3 on the Richter
scale. A more recent earthquake in California in 1989 registered 7.2. How much
more severe was the
earthquake in Tokyo in terms of the amplitude of its seismic wave?
2 The decibel scale
Noise level in decibels
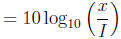
where I is the amplitude of a minimal audible sound wave and x is the
amplitude of another sound
wave. Read Text Example 2.3.3 (Pg 141).
3 The pH scale
pH value =
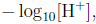
where [H+] is the concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution. Read Text Example 2.3.4 (Pg 142).
| Prev | Next |