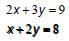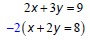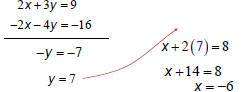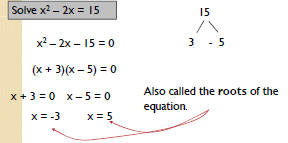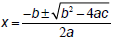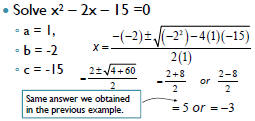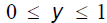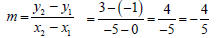GRE Review - Algebra
| Objectives • Students will be able to use the multiplication and addition principles together to solve linear equations Solve for x : 3x – 2 = 10 |
||||||||
| Example 3w + 4 = 5w − 6 |
||||||||
| Example 2(a − 3) = −5(2a +1) |
||||||||
Solving a system of linear equations
|
||||||||
| Solving Quadratics | ||||||||
|
Example Students will be able to • Solve equations by factoring
|
||||||||
| Example • If the quadratic 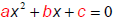 does doesnot factor, we will use the quadratic formula :
|
||||||||
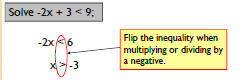
| Inequalities | ||||||||
| Example Students should be able to • solve linear inequalities
|
||||||||
| Double Inequalities • They will sometimes stipulate some constraints on a variable . 0 < y < 1
|
||||||||
| Applications • It would be impossible to cover the myriad of applications that could be on the test. I will go through the thought process on just one here. |
||||||||
| Example • Lex is twice as far from the finish line as he is from the start of 18 mile race. How far has he run? |
||||||||
| Methodology • Step 1. Read the problem. If you don’t understand it, read it again. If you still don’t understand it, read it a 3rd time. • Step 2. Identify the given information • Step 3. Identify what you are trying to find. • Step 4. Draw a picture if necessary to help you visualize the problem. • Step 5. Start labeling the drawing or setting up a formula to solve . • Step 6. Solve the problem. • Step 7. Make sure your answer makes sense. |
||||||||
| Example • Lex is twice as far from the finish line as he is from the start of 18 mile race. How far has he run?
|
||||||||
| Coordinate Geometry | ||||||||
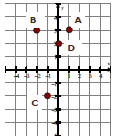
| Example ( Plotting Points ) • Plot the following pairs of points A (1, 3), B (-2, 3), C (-1, -2), D (0, 2).
|
||||||||
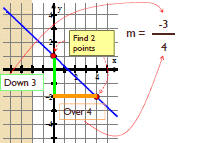
| Example Students should be able to • find the slope when given a line or points on the line
|
||||||||
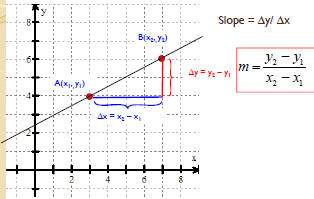
| Derivation of the slope formula
|
||||||||
| Example • Find the slope of the line containing the points (0,-1), (-5, 3)
|
||||||||
| Prev | Next |