Graphing Linear Inequalities
Today we're going to discuss
• Graphing inequalities involving lines.
• Graphing solutions to multiple linear inequalities .
• Setting up a collection of inequalities from a word problem.
• Solving the word problem using the graph of those inequalities.
1 Inequalities
We will be doing a bunch of work with inequalities, so it
will help to remember the rules
associated with inequalities.
associated with inequalities.
1. You can add (or subtract) a number from both sides of an inequality.
Example: Add 3x to both sides of the inequality -3x + y ≤ 6:
2. You can switch the sides of the inequality, if you also
switch the orientation of the
inequality sign (that is < becomes >).
Example: Switch the sides of the inequality 5 ≥ 3x + 7y:
3. You can multiply (or divide) an inequality by a
positive number (and this does not
change the orientation of the inequality sign).
Example: Divide the inequality 3y < 5x + 4 by 3.
4. You can multiply (or divide) an inequality by a
negative number , if you also switch
the orientation of the inequality sign.
Example: Divide the inequality -3y < 5x + 4 by -3:
2 Graphing Linear Inequalities
1. Graph x + y ≥ -2. First, graph the line x + y = -2.
Then, pick a point above the
line. Does that point satisfy x + y ≥ -2? If yes, color the region above the
line. If
not, color the region below the line.
2. If instead you wanted to graph x + y > -2, you draw a
dotted line instead of a solid
one. Then proceed as before.
We can do this for more than one inequality at once!
Example 1. Sketch the solution set for the
following system. Find the coordinates for the
vertices of the region (the coordinates lie at the intersection of lines, so we
can use rref on
the calculator to find these ).
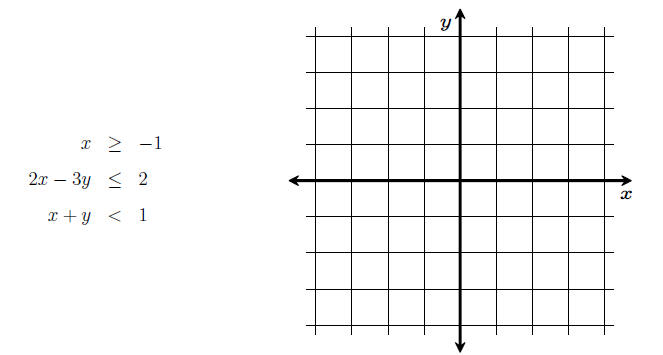
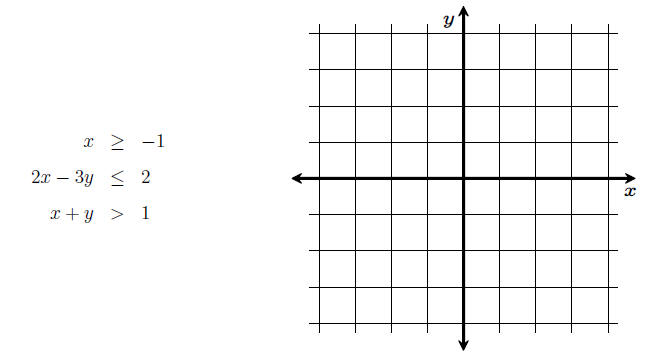
Example 2. Sketch the solution set for the system.
Find the coordinates for the vertices
of the region.
Definition 1. A solution set for a system of linear
inequalities is bounded if you can enclose
it by a circle. Otherwise, it is unbounded.
Questions: Is Example 1 bounded or unbounded? Is Example 2 bounded or unbounded?
3 Setting up linear inequality word problems
Definition 2. A linear programming problem consists
of:
1. a system of linear equations and inequalities, and
2. a linear function to be maximized of minimized.
The goal is to find the solution to the system of equations
and inequalities at which the
linear function is maximized (or minimized).
Linear programming problems are very common in real world
applications. The function to
be maximized (or minimized) is often profit or cost.
Example 3. It takes Mike 10 minutes to do an oil
change and 20 minutes to do a tire
change. He's working for 60 minutes today. He has enough tires in stock to
change them on
two cars , and he has enough oil to do 4 oil changes. If he can earn $10 per oil
change and
$40 per tire change, how many of each should he do to maximize profits?
Step 1: Make a table of information.
Step 2: Determine the function to maximize (or minimize).
Step 3: Set up the system of linear inequalities.
How can we solve a problem like this ? We'll need to find
the set of possible solutions (the
feasible solutions) and pick the best one (the optimal solution). We will use
the method
of corners.
4 Solving a linear programming problem
Step 4: Graph the inequalities. This is our feasible set.
Step 5: Find the vertices of the region. (We call these the corner points).
Step 6: Calculate the objective function at these points.
Step 7: Pick the maximum (or minimum).
This method is called the method of corners. It will always work when our set is bounded!
Note: If the set is unbounded there might not be a solution.
Note: If you can't create a feasible set, then the problem
is infeasible (also called inconsis-
tent.) For example, if the linear inequalities included x < 3 and x > 7, the
problem would
be infeasible.
We have leftover resources when there are items that we do
not use in the optimal solution.
Question: What are the leftover resources here?
5 Another Linear Programming Example
Example 4. Melanie is trying to learn Polish using
a workbook and some cassette tapes.
Each workbook page takes 1/2 an hour to do and each cassette takes 1 hour to
listen to. She
has 50 workbook pages and 4 cassette tapes. She can increase her vocabulary by 5
words
for each workbook page she does, and by 12 words for each cassette she listens
to. If she
can spend 10 hours trying to learn Polish this week, what should she do to
maximize her
vocabulary?
Step 1: Make a table of information.
Step 2: Determine the equation to maximize (or minimize).
Step 3: Set up the system of linear inequalities.
Step 4: Graph the inequalities.
Step 5: Find the corner points (vertices).
Step 6: Calculate the objective function at these points.
Step 7: Pick the maximum (or minimum).
Question: Are there any leftover resources?
| Prev | Next |