FINITE MATHEMATICS FOR BUSINESS AND MANAGEMENT
COURSE DESCRIPTION:
While this course may be used to fulfill part of the six-hour general education
mathematics requirement for the A.S. degree at John A. Logan College , it is
designed
primarily for economics majors, business administration, and accounting majors.
Those
students will be required to take a calculus course to complete their
mathematics
sequences. This course will fulfill the mathematics requirement for the A.A.
degree.
Topics covered include functions and lines, linear systems , linear programming,
the
Simplex Method, mathematics of finance, set theory, and probability. This course
is not
designed for mathematics or science majors. The Texas Instruments TI-83 graphing
calculator or a graphing calculator approved by the instructor is required for
this course.
PREREQUISITES:
MAT 108 with a grade of “C” or higher or assessment
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
1. Construct cost, revenue, and profit functions and perform break-even
analysis.
2. Solve straight-line depreciation problems utilizing linear functions.
3. Calculate future value and present value for simple interest accounts,
compound
interest accounts, and annuities.
4. Calculate effective rate of interest for a compound interest account.
5. Calculate the point of equilibrium in supply and demand analysis.
6. Write the parametric form of an infinite solution to a system of linear
equations.
7. Solve a system of linear equations using matrices and elementary row
operations.
8. Apply matrix operations in performing tests for equality, addition,
subtraction,
scalar multiplication, and matrix multiplication.
9. Calculate the inverse of a square matrix .
10. Utilize inverse matrices to aid in solving for the sector production levels
that will
meet internal and external demands of a Leontief Input-Output model.
11. Calculate the feasible region and its corner points relating to a system of
linear
inequalities involving two variables .
12. Use the feasible region and its corner points to solve a two-variable linear
programming problem.
13. Apply the Simplex Method to solve a linear programming problem involving
standard and mixed constraints.
14. Utilize the Dual to solve a linear programming problem.
15. Apply set operations and use Venn diagrams to aid in performing tests for
equality, unions, intersections, complements, and subset analysis.
16. Count the number of elements in a set using Venn diagrams, the
inclusionexclusion
principle, the addition rule , the multiplication rule, tree diagrams,
permutations, and combinations.
17. Calculate regular and conditional probabilities using set counting
procedures,
mutual exclusion, independence, the complement rule, the union rule, the
multiplication rule , and Bayes’ rule.
COURSE OUTLINE:
Topics to be covered in this course include:
I. FUNCTIONS AND LINES
A. Functions
B. Graphs and Lines
C. Mathematical Models and Applications of Linear Functions
II. MATHEMATICS OF FINANCE
A. Simple Interest
B. Compound Interest
C. Annuities and Sinking Funds
D. Present Value of an Annuity and Amortization
III. LINEAR SYSTEMS
A. Systems of Two Equations
B. Systems with Three Variables: An Introduction to a Matrix Representation of
a Linear System of Equations
C. Gauss-Jordan Method for General Systems of Equations
D. Matrix Operations
E. Multiplication of Matrices
F. The Inverse of a Matrix
G. Leontief Input-Output Model in Economics
IV. LINEAR PROGRAMMING
A. Linear Inequalities in Two Variables
B. Solutions of Systems of Inequalities: A Geometric Picture
C. Linear Programming: A Geometric Approach
D. Applications
V. LINEAR PROGRAMMING: THE SIMPLEX METHOD
A. Setting Up the Simplex Method
B. The Simplex Method
C. The Standard Minimum Problem: Duality
D. Mixed Constraints
E. Multiple Solutions, Unbounded Solutions, and No Solutions
VI. SETS AND COUNTING
A. Sets
B. Counting Elements in a Subset Using a Venn Diagram
C. Basic Counting Principles
D. Permutations
E. Combinations
F. A Mixture of Counting Problems
VII. PROBABILITY
A. Introduction to Probability
B. Equally Likely Events
C. Compound Events: Union, Intersection, and Complement
D. Conditional Probability
E. Independent Events
F. Bayes’ Rule
COURSE REQUIREMENTS:
Homework. Homework will be assigned at every class session. The student should
realize that , as a general rule of thumb , a minimum of two hours of study
outside of
class is required for every one hour of class time. This course will require a
minimum of
twelve to twenty-two hours per week of outside class work.
Attendance. Attendance to this class is both expected and required. John A.
Logan
College’s attendance policy will be enforced:
A. Students are expected to attend all scheduled class periods for the courses
in
which they are enrolled unless they are participating in a scheduled, supervised
college trip or function. There are no excused absences or minimum number of
class “cuts.” All absences must be made up in a manner acceptable to the
instructor.
B. A student who is absent from class for three consecutive meetings or who is
excessively absent as defined by the instructor (more than 5 absences), without
prior approval, may be required by the instructor to meet with the appropriate
administrator before being readmitted to the class. Students who claim illness
as
a cause for excessive absences may be required to present a physician’s
statement before being readmitted to the class.
Required Materials. The textbook, along with the usual notebook, paper, pencils,
etc.
represent the required materials for the class. The utilization of the Texas
Instruments
TI-83 Graphing Calculator will be emphasized in classroom presentations as well
as on
homework assignments and tests. Hence, the student is required to use the TI-83
on
appropriate assignments and should be knowledgeable of its workings. The
functions
provided by the Texas Instruments TI-83 Graphing Calculator will be
utilized
throughout the course and will be required for successful completion of
certain
homework assignments and tests.
Student Success Center. Tutors may be obtained through the Student Success
Center.
Contact the staff in C219 if this service is desired. John A. Logan College will
make
reasonable accommodations for students with documented disabilities under
Section
504 of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973, and the Americans with Disabilities Act
of 1990.
Any student with a disability that may have some impact on work in this class,
who feels
she/he needs an accommodation, should make an appointment with the Coordinator
of
Services for Students with Disabilities on campus, Christy McBride, Room C219B,
Ext.
8516. Before services can be provided, this advisor must determine eligibility
and
arrange appropriate academic adjustments. It is the student’s responsibility
to
register in advance of a school term with this office and to turn in a schedule
each term to ensure that there is every opportunity for success in this class.
English Writing Center/Tutoring: For assistance with writing assignments in any
college
courses, students are encouraged to visit “The Write Place” in E109. English
instructors
are available for one-on-one tutoring each semester during hours posted at the
center.
Financial Aid. Students who receive financial assistance and completely withdraw
from
classes prior to 60% of the semester being completed (approximately 2-3 weeks
after
midterm) could be responsible to return a portion of their Federal Pell Grant
award.
Prior to withdrawing from courses, students should contact the Financial Aid
Office.
METHOD OF EVALUATION:
Evaluation will be made on the basis of:
1. A maximum of five 100-point exams that will be administered periodically over
the course of the semester.
2. A 200-point comprehensive final exam.
The combined average of the tests and the final exam will determine the
student’s
overall course percentage grade.
No make-ups will be given on the tests. Students attending a required
school-sponsored
activity must make arrangements with the instructor to complete the exam
before attending the obligatory event. Any answers, which have been copied from
someone else, will result in a zero for all parties involved.
Grades are assigned according to the following scale:
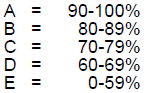
METHOD OF PRESENTATION:
Most instruction will be of the lecture-discussion type. Homework will be
assigned
which, together with announced exams serve to amplify and clarify the classroom
discussions. Occasionally, topics will be assigned to be performed through
independent
study. Ample opportunity will be provided for the student to meet with the
instructor on
a one-to-one basis during office hours to clear up any difficulties that may
arise.
TEXT:
Finite Mathematics, Fifth Edition: by Rolf; Harcourt, Inc.; 2002.
INSTRUCTOR:
Scott Elliott
Office: E209G
Ext.: 8394
DATE: Summer, 2005
| Prev | Next |