Factoring Special Products
Perfect Square Trinomials
| Perfect Square Trinomials
a2 + 2ab + b2 = (a + b)2 |
In order for a polynomial to be a perfect square
trinomial , two conditions must be satisfied:
1. The first and last terms must be perfect squares.
2. The “ middle term ” must equal 2 or – 2 times the
product of the expressions being squared in the
first and last term.
Example: Factor the following :
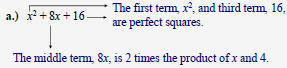
x2 + 8x + 16 = (x + 4)2
b.) 9x4 − 30x2z + 25z2
9x4 − 30x2z + 25z2 = (3x2 – 5z)2
| Difference of Two Squares a2 – b2 = (a + b)(a − b) |
Example: Factor the following :
a.) 3x2 − 27
3x2 − 27 = 3(x2 – 9) 3 is a common factor.
= 3(x + 3)(x – 3)
b.) 4x2 − 25y4
4x2 − 25y4 = (2x + 5y2)(2x – 5y2)
The Sum of Two Cubes
| The Sum of Two Cubes a3 + b3 = (a + b) (a2 − ab + b2) |
Example: Factor: 27x3 + 125
a = 3x
b = 5
27x3 + 125 = (3x)3 + 53
= (3x + 5) [(3x)2 − 3x·5 + 52]
= (3x + 5)(9x2 − 15x + 25)
| The Difference of Two Cubes a3 − b3 = (a − b) (a2 + ab + b2) |
Example: Factor: x3 − 64
a = x
b = 4
x3 − 64 = x3 – 43
= (x − 4) (x2 + 4x + 42)
= (x − 4) (x2 + 4x + 16)
Practice
Factor each perfect square trinomial completely
x2 + 14x + 49
x2 − 8x + 16
4a2 − 12ab + 9b2
4x2 + 20x + 25
n2 − 16
a4 − 16
36 p2 − 49q2
9x6 − 25y8
64x3 + 1
8x3 − 27
4x4 − 4xy3
125a6 + 8b3
| Prev | Next |