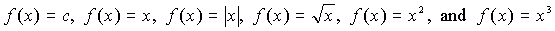| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | |
simplifying square roots with exponents ,
solved sample papers for class viii of chapter square and square roots,
simplifying radical expressions solver ,
difference between evaluation & simplification of an expression,
solving second order non homogeneous differential equations ,
quadratic equations vertex and standard form online calculators ,
algebra 2, vertex form of a linear equation ,
interactive games solve a quadratic equation by completing the square ,
solve non homogeneous first order partial differential equation ,
integer adding,subtracting,multiplying, dividing worksheet ,
symbolic method math formula solving,
calculator texas instruments convert decimals into fractions ,
simultaneous equation solver quadratic 3 unknowns ,
maths, algebra balancing linear equations,
solving simultaneous nonlinear equations matlab ,
ways to cheat on dividing a decimal by a whole number ,
Educational games solve a quadratic equation by completing the square ,
square root simplify equations calculator ,
how to calculate greatest common divisor ,
convert decimal to radical fraction expression,
finding the least common denominator algebra ,
factor calculator for a quadratic equation ,
factoring a difference of squares lesson plan for algebra 2 ,
square root calculator using simplified radical ,
solving linear equation cheats ,
factor polynomial college algebra two variable ax by ,
Solving Non linear differential equations ,
writing linear equations powerpoint presentation ,
exponent definition quadratic hyperbola parabola ,
a help sheet explaining how to solve equations by balancing them ,
easy addition and subtraction of algebraic expressions ,
Solving simultaneous algebra equations
Thank you for visiting our site! You landed on this page because you entered a search term similar to this:
solve and graph non liner system of equations, here's the result:
- Understand the
Cartesian coordinate system and the idea of locating ordered
pairs of numbers.
- Know and use the
mid-point and distance formulas to solve real world problems.
- Know how to graph
relations in the coordinate plane.
- Find domain
and range of a relation from a list or ordered pairs, graph or
a table of values.
- Recognize and
evaluate basic features of a graph of a relation.
- Produce graphs
of simple relations using tables.
- Find the x
and y-intercepts of the graph of an equation (algebraically and
graphically)
- Determine the
symmetry of the graph of an equation (algebraically and graphically)
- Write the General
Form Equation of a circle in Standard Form and determine the center
and radius of the circle
|
Basic Features
of a Graph
- domain and
restricted values
- range
- x
and y intercepts
- intervals
where a graph is constant, increasing or decreasing
|
|
Linear Equations and Inequalities
- Solve linear
equations algebraically and graphically.
- Deal with fractional
coefficients in equations.
- Solve equations
involving absolute value algebraically.
- Solve a formula
for a given variable.
- Solve word problems
by setting up and solving a linear equation in one variable.
- Solve linear inequalities
in one variable including compound inequalities and inequalities involving
absolute value algebraically.
- Represent (graph or
plot) solution sets of inequalities on the number line.
Quadratic Equations
- Solve quadratic
equations by a variety of methods.
- Use the discriminant
to understand when a quadratic has no, one or two real roots algebraically.
- Solve simple word
problems using quadratic equations
- Construct and
use a quadratic model to solve an application problem
|
Methods of
Solving Quadratics
- By factoring
and Using Zero Factor Property when possible.
- By extracting
square roots
- By completing
the square
- Using the
Quadratic formula
|
|
Polynomials and Polynomial
Expressions
- Perform basic
operations with polynomials (add, subtract, multiply including
FOIL)
- Use formulas for
these special products:
- Factor polynomials
by factoring out the Greatest Common Factor,
by grouping, and by using special products formulas for trinomials
- Factor simple
trinomials of form a x2 + b x + c
by guess-and-check or by grouping
- Solve simple equations
using the Zero Factor Property when possible.
- Solve polynomial
inequalities (degree > 1)
|
The
Special products:
- (a
+ b)2
- (a
- b)2
- (a
+ b)(a - b)
|
|
Solving
Non-linear Inequalities
- Use
critical numbers to determine test intervals for a polynomial
inequality
- Solve
a polynomial inequality algebraically and graphically
- Construct
and use a polynomial inequality to solve an application
problem
|
|
|
Rational Expressions
- Know how to decide the
domain of a rational expressions. (Decide what values are excluded by the
denominator.)
- Simplify and perform
basic operations involving rational expressions (addition, subtraction, multiplication,
division)
- Find a Least Common
Denominator and use it to add or subtract rational expressions.
- Solve equations with
rational expressions. Recognize that some solutions may be extraneous and
check for that.
- Within the context of
sections covered, apply rational expressions to simple situations.
Other Types of
Equations and Inequalities
- Solve equations involving
radicals or rational exponents
- Solve equations involving
rational fractions
- Solve equations involving
absolute values
- Solve higher degree
polynomial equations by factoring
- Solve equations methods
as appropriate.
Equations of the
Line and Linear Inequalities
| |
Representations
of a line:
- Standard
form: A x + B y =
C where A, B, and C are any real numbers.
- Slope-intercept
form: y = m x + b
where m is the slope of a line and b is the y-intercept.
- Point-slope
form: y - k = m (x - h)
where (h,k) is any point on the line.
|
|
Special Slope
Relationships.
- Horizontal
lines (m = 0)
- Vertical
lines (m is undefined)
- Parallel
lines (m1 = m2)
- Perpendicular
lines (m1 m2 = -1)
|
|
General Function
Concepts
Definition and Notation
- Determine if an
equation or a set of ordered pairs represents a function
- Use function notation
- Evaluate a function
- Find the domain
of a function
- Create and apply
a piecewise-defined function.
- Interpret input
and output of real-life functions
- Solve an application
problem involving real-life functions
Graphs of functions
- Find domain and
range using the graph of a function
- Vertical Line Test
- Describe the increasing
and decreasing behavior of a function
- Classify a function
as even or odd
- Identify six common
graphs
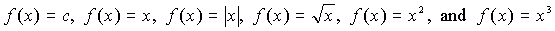
Transformations
of Functions
- Sketch the graph
of a function using common graphs and transformations
- Write the equation
of function using common graphs and transformations
Algebra of Functions
- Find the sum, difference,
product, and quotient of functions
- Find the composition
of two functions and determine the domain and range
- Identify a function
as the composition of two functions
- Solve real-life
problems involving combinations and composition of functions
Inverse Functions
- Determine if a
function has an inverse function (Horizontal Line Test)
- Find the Inverse
of a function
- Graph a function
and its Inverse (Know that the graph of f
-1 is a reflection of the
graph of f across the line y
= x.)
Polynomial Functions
Polynomial division
- Divide polynomials
using long division
- Divide polynomials
using Synthetic division
- Use the Remainder
Theorem to evaluate a polynomial
- Use the Factor
Theorem to factor a polynomial
Complex numbers (if
covered by your instructor)
- Perform operations
with complex numbers and write the results in standard form
- Solve a quadratic
equation involving complex zeros
Polynomial analysis
Rational Functions
- Find the domain of
a rational function
- Find the vertical
and horizontal asymptotes of the graph of a rational function
- Sketch the graph
of a rational function
- Use a rational function
model to solve an application problem
Exponential Functions
- Sketch the graph
of an exponential function
- Investigate basic
characteristics of an exponential function (domain, range, intercepts, increasing/decreasing
behavior)
- Write formulas of
transformed exponential functions
- Use an exponential
model to solve an application problem (in particular, models involving the
natural exponential function)
- Use the compound
interest formula to solve finance problems
- Construct and use
a model for exponential growth or exponential decay
Logarithmic Functions
- Properties of logarithms
- Solve Logarithmic
and Exponential Equations
- Sketch the graph
of a logarithmic function
- Investigate basic
characteristics of a logarithmic function (domain, x-intercept, vertical
asymptote)
- Write formulas of
transformed logarithmic functions
- Use a logarithmic
model to solve an application problem (in particular, models involving the
natural logarithmic function)
Systems in two variables
- Solve a linear
system of equations
- Construct and
use a linear system of equations to solve an application problem
- Solve nonlinear
systems
- Construct and
use a nonlinear system of equations to solve an application problem
|
Methods of
Solving Systems.
- by substitution
- by elimination
- graphically
|
|