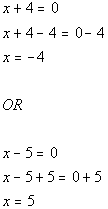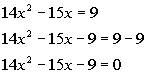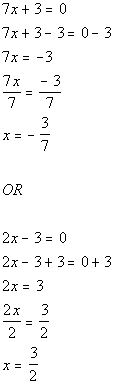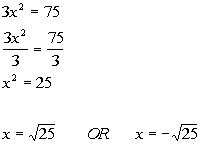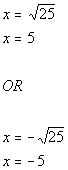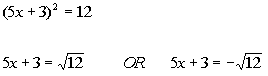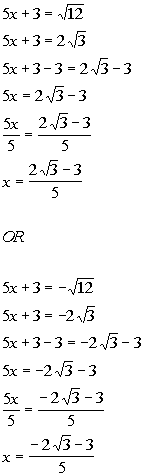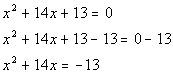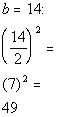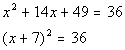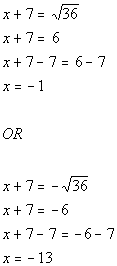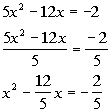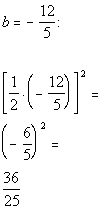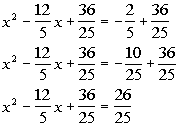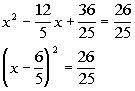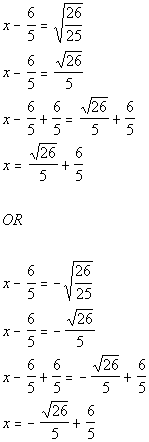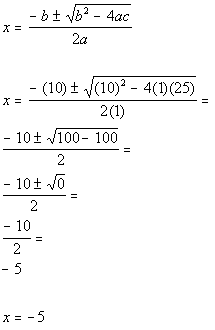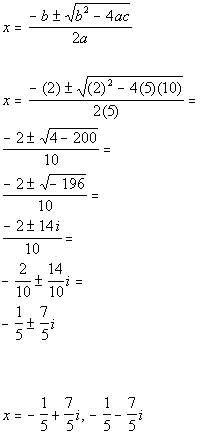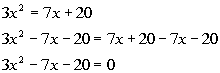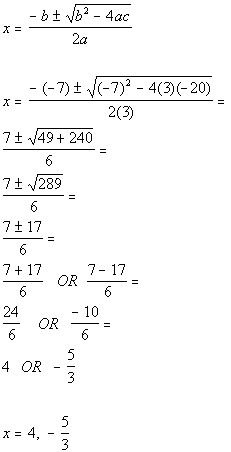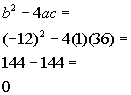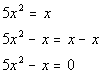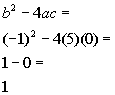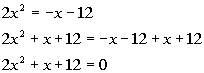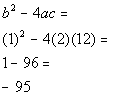College Algebra
Answer/Discussion to Practice
Problems
on Quadratic Equations
 Answer/Discussion
to 1a Answer/Discussion
to 1a
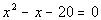
|
| Step 1: Simplify
each side if needed. |
| This quadratic equation is already simplified. |
Step 2: Write
in standard form, 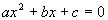 ,
if needed. ,
if needed. |
| This quadratic equation is already in standard form. |
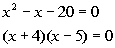 |
*Quad. eq. in standard form
*Factor
the trinomial |
| Step 4: Use the
Zero-Product
Principle
AND
Step 5: Solve for the
linear
equation(s) set up in step 4. |
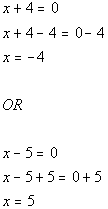 |
*Use Zero-Product Principle
*Solve the first linear equation
*Solve the second linear equation
|
| There are two solutions to this quadratic equation: x
=
-4 and x = 5. |
 Answer/Discussion
to 1b Answer/Discussion
to 1b
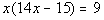
|
| Step 1: Simplify
each side if needed. |
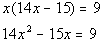 |
*Use Dist. Prop. to clear the ( ) |
Step 2: Write
in standard form, 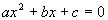 ,
if needed. ,
if needed. |
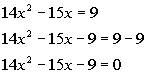 |
*Inverse of add. 9 is sub. 9
*Quad. eq. in standard form |
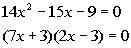 |
*Quad. eq. in standard form
*Factor
the trinomial |
| Step 4: Use the
Zero-Product
Principle
AND
Step 5: Solve for the
linear
equation(s) set up in step 4. |
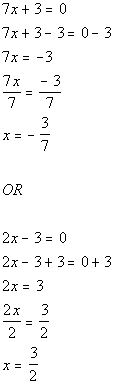 |
*Use Zero-Product Principle
*Solve the first linear equation
*Solve the second linear equation
|
| There are two solutions to this quadratic equation: x
=
-3/7 and x = 3/2. |
 Answer/Discussion
to 2a Answer/Discussion
to 2a
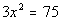
|
| Step 1: Write
the quadratic equation in the form
if needed
AND
Step 2: Apply the
square
root method. |
Note how this quadratic equation is not in the form 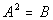 to begin with. The 3 is NOT part of the expression being squared
on the left side of the equation. We can easily write it in the form
to begin with. The 3 is NOT part of the expression being squared
on the left side of the equation. We can easily write it in the form 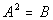 by dividing both sides by 3.
by dividing both sides by 3. |
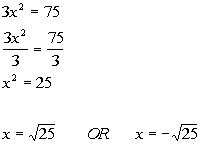 |
*Not in the form 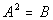
*Inv. of mult. by 3 is div. by 3
*Written in the form 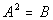
*Apply the sq. root method
*There are 2 solutions |
| Step 3: Solve for the
linear equation(s) set up in step 2. |
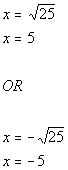 |
*Sq. root of 25 = 5
*Neg. sq. root of 25 = -5
|
| There are two solutions to this quadratic equation: x
=
5 and x = -5. |
 Answer/Discussion
to 2b Answer/Discussion
to 2b
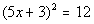
|
| Step 1: Write
the quadratic equation in the form
if needed
AND
Step 2: Apply the
square
root method. |
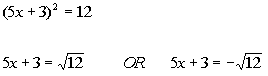 |
*Written in the form 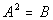
*Apply the sq. root method
*There are 2 solutions |
| Step 3: Solve for the
linear equation(s) set up in step 2. |
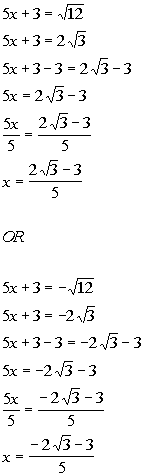 |
*Sq. root of 12 = 2 sq. root of 3
*Solve for x
*Neg. sq. root of 12 = -2 sq. root of 3
*Solve for x
|
There are two solutions to this quadratic equation: x
= 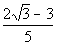 and x =
and x = 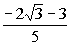 . . |
 Answer/Discussion
to 3a Answer/Discussion
to 3a
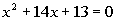
|
| Step 1: Make
sure that the coefficient
on the
term is equal to 1. |
The coefficient of the 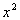 term is already 1.
term is already 1. |
Step 2: Isolate
the 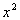 and x
terms. and x
terms. |
Note how the 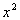 and x terms are not isolated to begin with.
We can easily fix that by moving the constant to the other side of the
equation.
and x terms are not isolated to begin with.
We can easily fix that by moving the constant to the other side of the
equation. |
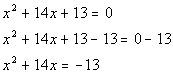 |
*Inverse of add. 13 is sub. 13
* and x terms are now isolated
and x terms are now isolated
|
| Step 3: Complete
the square. |
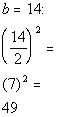 |
*b is the coefficient
of the x term
*Complete the square by taking 1/2 of b
and squaring it
|
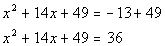 |
*Add constant found above to BOTH sides of
the eq.
*This creates a PST on the left side of eq. |
| Step 4: Factor
the perfect square trinomial (created in step 3) as a binomial squared. |
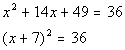 |
*Factor the PST |
| Step 5: Solve
the equation in step 4 by using the square
root method. |
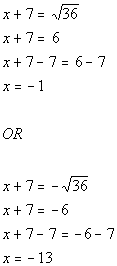 |
*Written in the form 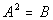
*Apply the sq. root method
*There are 2 solutions
|
| There are two solutions to this quadratic equation: x
=
-1 and x = -13. |
 Answer/Discussion
to 3b Answer/Discussion
to 3b
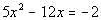
|
| Step 1: Make
sure that the coefficient
on the
term is equal to 1. |
Note how the coefficient on the 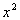 term is not 1 to begin with. We can easily fix that by dividing both
sides by that coefficient, which in this case is 5 .
term is not 1 to begin with. We can easily fix that by dividing both
sides by that coefficient, which in this case is 5 . |
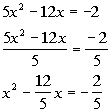 |
*Divide both sides by 5
*Coefficient of 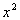 term is now 1
term is now 1
|
Step 2: Isolate
the 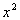 and x
terms. and x
terms. |
The 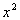 and
x
terms
are already isolated. and
x
terms
are already isolated. |
| Step 3: Complete
the square. |
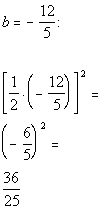 |
*b is the coefficient of the x
term
*Complete the square by taking 1/2 of b
and squaring it
|
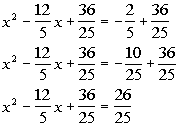 |
*Add constant found above to BOTH sides of
the eq.
*This creates a PST on the left side of eq.
|
| Step 4: Factor
the perfect square trinomial (created in step 3) as a binomial squared. |
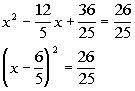 |
*Factor the PST |
| Step 5: Solve
the equation in step 4 by using the square
root method. |
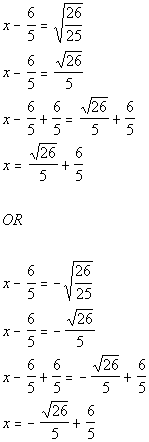 |
*Written in the form 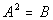
*Apply the sq. root method
*There are 2 solutions
|
There are two solutions to this quadratic equation: x
= 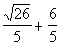 and x =
and x = 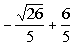 . . |
 Answer/Discussion
to 4a Answer/Discussion
to 4a
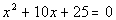
|
| Step 1: Simplify
each side if needed. |
| This quadratic equation is already simplified. |
Step 2: Write
in standard form, 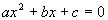 ,
if needed. ,
if needed. |
| This quadratic equation is already in standard form. |
| Step 3: Identify
a,
b,
and c. |
| a, the number in front of x
squared, is 1.
b, the number in front of x,
is 10.
c, the constant, is 25.
Make sure that you keep the sign that is in front of each of these numbers.
Next we will plug it into the quadratic formula. Note that
we are only plugging in numbers, we don't also plug in the variable. |
| Step 4: Plug the
values found in step 3 into the quadratic
formula
AND
Step 5: Simplify if possible. |
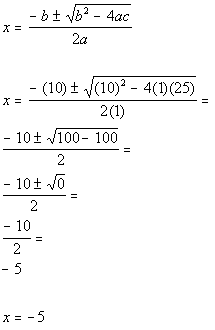 |
*Quadratic formula
*Plug in values found above for a,
b,
and c
*Simplify
|
 Answer/Discussion
to 4b Answer/Discussion
to 4b
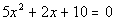
|
| Step 1: Simplify
each side if needed. |
| This quadratic equation is already simplified. |
Step 2: Write
in standard form 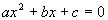 if needed.
if needed. |
| This quadratic equation is already in standard form. |
| Step 3: Identify
a,
b,
and c. |
| a, the number in front of x
squared, is 5.
b, the number in front of x,
is 2.
c, the constant, is 10.
Make sure that you keep the sign that is in front of each of these numbers.
Next we will plug it into the quadratic formula. Note that
we are only plugging in numbers, we don't also plug in the variable. |
| Step 4: Plug the
values found in step 3 into the quadratic
formula
AND
Step 5: Simplify if possible. |
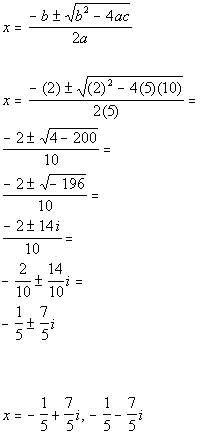 |
*Quadratic formula
*Plug in values found above for a,
b,
and c
*Simplify
*Square
root of a negative 1 is i
|
 Answer/Discussion
to 4c Answer/Discussion
to 4c
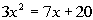
|
| Step 1: Simplify
each side if needed. |
| This quadratic equation is already simplified. |
Step 2: Write
in standard form 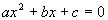 if needed.
if needed. |
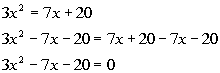 |
*Inverse of add. 7x
and 20 is sub. 7x and 20
*Quad. eq. in standard form |
| Step 3: Identify
a,
b,
and c. |
| a, the number in front of x
squared, is 3.
b, the number in front of x,
is -7.
c, the constant, is -20.
Make sure that you keep the sign that is in front of each of these numbers.
Next we will plug it into the quadratic formula. Note that
we are only plugging in numbers, we don't also plug in the variable. |
| Step 4: Plug the
values found in step 3 into the quadratic
formula
AND
Step 5: Simplify if possible. |
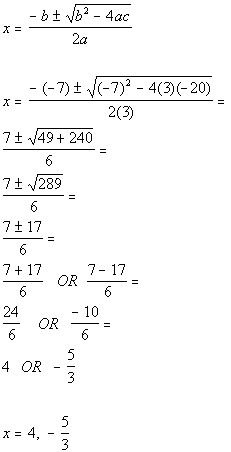 |
*Quadratic formula
*Plug in values found above for a,
b,
and c
*Simplify
|
 Answer/Discussion
to 5a Answer/Discussion
to 5a
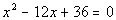
|
| Step 1: Simplify
each side if needed. |
| This quadratic equation is already simplified. |
Step 2: Write
in standard form, 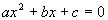 ,
if needed. ,
if needed. |
| This quadratic equation is already in standard form. |
| Step 3: Identify
a,
b,
and c. |
| a, the number in front of x
squared, is 1.
b, the number in front of x,
is -12.
c, the constant, is 36.
Make sure that you keep the sign that is in front of each of these numbers. |
Step 4: Plug the
values found in step 3 into the discriminant, 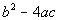 , ,
AND
Step 5: Simplify if possible. |
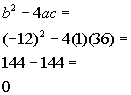 |
*Discriminant formula
*Plug in values found above for a,
b,
and c
*Discriminant |
| Since the discriminant is zero, that means there is only one real
number solution. |
 Answer/Discussion
to 5b Answer/Discussion
to 5b
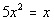
|
| Step 1: Simplify
each side if needed. |
| This quadratic equation is already simplified. |
Step 2: Write
in standard form, 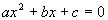 ,
if needed. ,
if needed. |
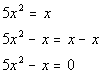 |
*Inverse of add. x
is sub. x
*Quad. eq. in standard form |
| Step 3: Identify
a,
b,
and c. |
| a, the number in front of x
squared, is 5.
b, the number in front of x,
is -1.
c, the constant, is 0.
Note that since the constant is missing it is understood to be 0.
Make sure that you keep the sign that is in front of each of these numbers. |
Step 4: Plug the
values found in step 3 into the discriminant, 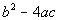 , ,
AND
Step 5: Simplify if possible. |
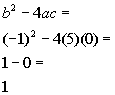 |
*Discriminant formula
*Plug in values found above for a,
b,
and c
*Discriminant |
| Since the discriminant is a positive number, that means there are
two distinct real number solutions. |
 Answer/Discussion
to 5c Answer/Discussion
to 5c
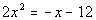
|
| Step 1: Simplify
each side if needed. |
| This quadratic equation is already simplified. |
Step 2: Write
in standard form, 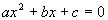 ,
if needed. ,
if needed. |
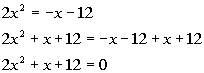 |
*Inverse of sub. x and
12 is add. x and 12
*Quad. eq. in standard form |
| Step 3: Identify
a,
b,
and c. |
| a, the number in front of x
squared, is 2.
b, the number in front of x,
is 1.
c, the constant, is 12.
Make sure that you keep the sign that is in front of each of these numbers. |
Step 4: Plug the
values found in step 3 into the discriminant, 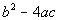 , ,
AND
Step 5: Simplify if possible. |
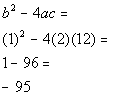 |
*Discriminant formula
*Plug in values found above for a,
b,
and c
*Discriminant |
| Since the discriminate is a negative number, that means there are
two distinct complex imaginary solutions. |
All contents
July 7, 2002 |